As a supplier of Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures, I've had the privilege of delving deep into the intricacies of their control systems. In this blog, I'll share my insights on what the control system of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is like, exploring its components, functions, and significance in the welding process.
Components of the Control System
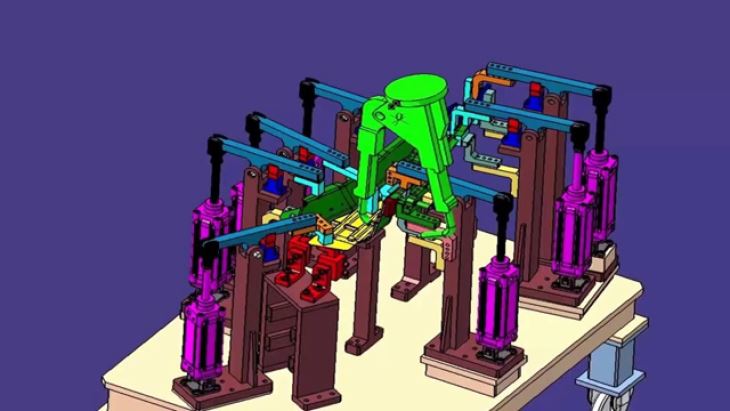
The control system of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is a complex network of hardware and software components that work together to ensure precise and efficient welding operations. At the heart of the system is the controller, which serves as the brain of the fixture. The controller is responsible for receiving input from various sensors, processing this information, and sending commands to the robotic arm and other components of the fixture.
One of the key components of the control system is the robotic arm. The robotic arm is a highly flexible and precise device that can be programmed to perform a wide range of welding tasks. It is equipped with multiple joints and axes of motion, allowing it to reach different positions and angles with ease. The controller sends commands to the robotic arm, specifying the path, speed, and orientation of the welding torch.
In addition to the robotic arm, the control system also includes a welding power source. The welding power source provides the electrical energy required for the MIG welding process. It is controlled by the controller, which adjusts the voltage, current, and other parameters to ensure consistent and high-quality welds. The controller also monitors the welding process in real-time, making adjustments as needed to compensate for variations in the workpiece or other factors.
Another important component of the control system is the fixture itself. The fixture is designed to hold the workpiece in place during the welding process, ensuring accurate and repeatable welds. It is typically equipped with clamps,定位 pins, and other devices to secure the workpiece and prevent it from moving. The controller can also be programmed to control the operation of the fixture, such as opening and closing the clamps or adjusting the position of the定位 pins.
Functions of the Control System
The control system of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture performs several important functions that are essential for the success of the welding process. One of the primary functions is to control the movement of the robotic arm. The controller uses a combination of sensors and algorithms to determine the optimal path and speed for the robotic arm to follow. It takes into account factors such as the shape and size of the workpiece, the location of the weld joints, and the desired welding parameters.
Another important function of the control system is to monitor the welding process. The controller continuously monitors the voltage, current, and other parameters of the welding power source, as well as the position and orientation of the robotic arm. It compares these values to the desired setpoints and makes adjustments as needed to ensure that the welding process is operating within the specified limits. If any abnormalities are detected, the controller can automatically stop the welding process and alert the operator.
The control system also plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of the welds. It can be programmed to perform various quality control functions, such as monitoring the weld bead width, penetration, and porosity. The controller can also use sensors to detect defects in the weld, such as cracks or incomplete fusion, and take appropriate action to correct them.
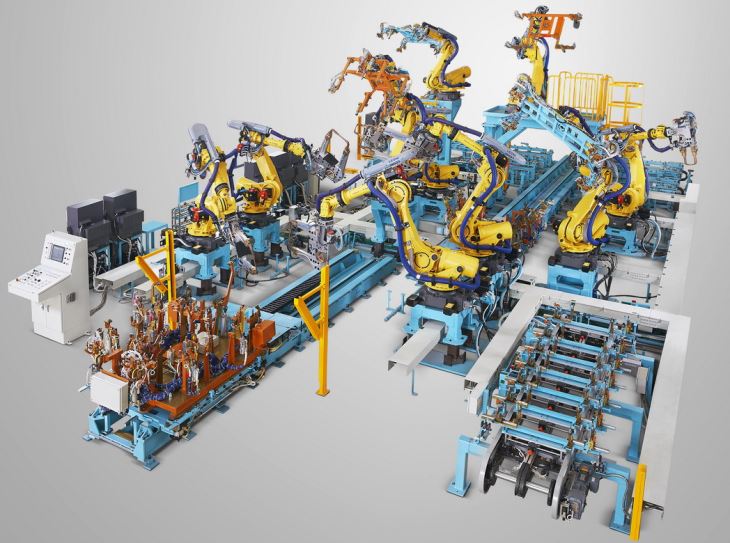

In addition to these functions, the control system can also be used to optimize the efficiency of the welding process. It can be programmed to perform tasks such as preheating the workpiece, cleaning the welding torch, and changing the welding wire automatically. These features can help to reduce the cycle time and increase the productivity of the welding operation.
Significance of the Control System
The control system of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is of great significance in the welding industry. It offers several advantages over traditional manual welding methods, including increased precision, consistency, and productivity. By using a robotic arm to perform the welding tasks, the control system can achieve a higher level of accuracy and repeatability than human operators. This results in better-quality welds and fewer defects, which can lead to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
The control system also allows for greater flexibility in the welding process. It can be programmed to perform a wide range of welding tasks, including complex and irregular shapes. This makes it suitable for use in a variety of industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. The ability to quickly and easily change the welding program also allows for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
Another advantage of the control system is its ability to improve the safety of the welding operation. By using a robotic arm to perform the welding tasks, the operator can be kept at a safe distance from the welding arc and other hazards. The control system also includes various safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and safety interlocks, to prevent accidents and protect the operator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the control system of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is a highly sophisticated and complex system that plays a crucial role in the welding process. It consists of several components, including the controller, robotic arm, welding power source, and fixture, which work together to ensure precise and efficient welding operations. The control system performs several important functions, such as controlling the movement of the robotic arm, monitoring the welding process, ensuring the quality of the welds, and optimizing the efficiency of the operation. Its significance in the welding industry cannot be overstated, as it offers several advantages over traditional manual welding methods, including increased precision, consistency, productivity, flexibility, and safety.
If you are interested in learning more about our Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures or would like to discuss your specific welding needs, please feel free to contact us. We would be happy to provide you with more information and help you find the right solution for your application. You can also visit our website to explore our Robotic Welding Fixture Line and Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture products.
References
- Groover, M. P. (2010). Automation, Production Systems, and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing. Prentice Hall.
- O'Neill, J. (2015). Welding Handbook, Volume 1: Welding Science and Technology. American Welding Society.
- Welder's Handbook: A Guide to Arc Welding and Related Processes. (2018). Lincoln Electric.



