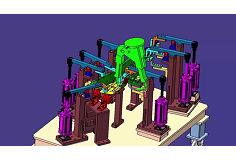
As a leading rear seats welding jig supplier, I've witnessed firsthand the diverse needs and preferences in the automotive manufacturing industry. One of the most common questions we encounter is about the differences between manual and automatic rear seats welding jigs. In this blog post, I'll delve into the key disparities, advantages, and disadvantages of each type, helping you make an informed decision for your production line.
Design and Structure
Manual rear seats welding jigs are typically simpler in design. They are often constructed with a basic frame that holds the rear seat components in place during the welding process. The operator manually positions the parts, adjusts the clamps, and initiates the welding. These jigs are usually made of sturdy metals like steel or aluminum, providing a stable platform for welding.
On the other hand, automatic rear seats welding jigs are more complex. They are equipped with advanced robotic arms, sensors, and control systems. The design of these jigs is optimized for high - speed and precision welding. The robotic arms can move in multiple axes, allowing for more intricate welding patterns. The sensors are used to detect the position and alignment of the parts, ensuring accurate welding every time.
Operation Process
The operation of manual rear seats welding jigs is highly dependent on the skills and experience of the operator. The operator must first load the rear seat components onto the jig, carefully align them according to the welding requirements. Then, they use manual tools to tighten the clamps and secure the parts. After that, the welding equipment is turned on, and the operator controls the welding process, moving the welding torch along the seams. This process requires a high level of concentration and dexterity from the operator.
In contrast, automatic rear seats welding jigs operate with minimal human intervention. Once the program is set up, the robotic arms automatically pick up the parts from the feeding system, place them in the correct position on the jig, and start the welding process. The control system monitors the entire process, making real - time adjustments to ensure the quality of the welds. The operator's role is mainly to oversee the operation, load the raw materials, and perform routine maintenance.
Welding Precision
Manual welding jigs can achieve a reasonable level of precision, but it largely depends on the operator's proficiency. Even the most skilled operators may have slight variations in their welding technique, which can lead to minor differences in the weld quality from one part to another. Factors such as fatigue, distractions, or changes in the welding environment can also affect the precision.
Automatic welding jigs, on the other hand, offer consistent and high - precision welding. The robotic arms can repeat the same welding motion with an extremely high degree of accuracy, typically within a few millimeters. The sensors and control systems ensure that the parts are always in the correct position, and the welding parameters are precisely controlled. This results in a more uniform and high - quality weld across all the rear seats produced.
Production Efficiency
Manual rear seats welding jigs are generally slower in terms of production rate. The time taken for each welding cycle includes the time for loading and unloading the parts, aligning them, and performing the actual welding. Since the process is manual, the speed is limited by the operator's physical capabilities.
Automatic welding jigs are much faster. They can complete a welding cycle in a fraction of the time it takes for a manual jig. The high - speed robotic arms can move quickly between different welding points, and the automated feeding system ensures a continuous supply of parts. This significantly increases the production output, making them ideal for large - scale manufacturing.
Cost Considerations
The initial investment for manual rear seats welding jigs is relatively low. The cost of the jig itself is usually affordable, and there is no need to purchase expensive robotic equipment or control systems. Additionally, the training cost for operators is also relatively low, as the operation is not overly complex.
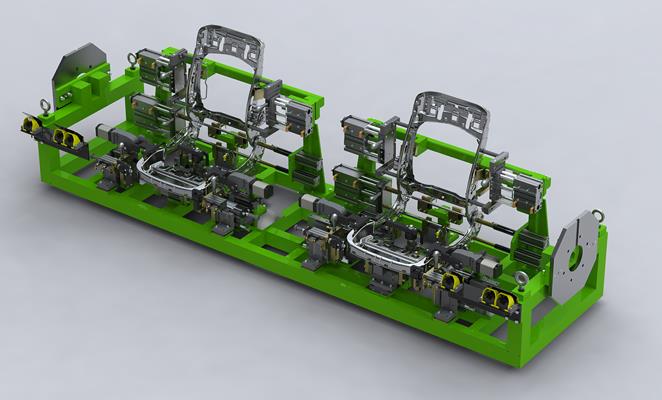

However, the long - term cost of manual welding jigs can be higher. The labor cost is a significant factor, especially in regions with high wage rates. Also, the potential for human error may lead to higher rejection rates, which increases the cost of production.
Automatic rear seats welding jigs require a substantial upfront investment. The cost of the robotic arms, sensors, control systems, and the jig itself is quite high. There is also a need for specialized training for the operators to set up and maintain the system. But in the long run, they can be more cost - effective. The high production efficiency reduces the labor cost per unit, and the low rejection rate saves on the cost of rework and waste.
Flexibility
Manual rear seats welding jigs offer a certain degree of flexibility. If there are minor changes in the design of the rear seats, the operator can easily adjust the position of the parts and the welding process. This makes them suitable for small - batch production or when there are frequent design changes.
Automatic welding jigs are less flexible in terms of quick design changes. Modifying the program for the robotic arms and the control system can be time - consuming and requires technical expertise. However, they are highly efficient for mass - producing a single design of rear seats.
Safety
Manual welding operations pose several safety risks to the operator. Exposure to welding fumes, intense light, and heat can cause health problems such as respiratory issues, eye damage, and burns. The use of manual tools also increases the risk of physical injuries.
Automatic welding jigs are generally safer. The robotic arms and the enclosed working environment reduce the operator's exposure to hazardous substances and high - energy welding processes. The control system can also detect abnormal conditions and stop the operation immediately, preventing potential accidents.
Industry Applications
Manual rear seats welding jigs are commonly used in small - scale automotive workshops or for custom - made rear seats. They are also suitable for industries where the production volume is low and the flexibility to change the design is important.
Automatic rear seats welding jigs are widely used in large - scale automotive manufacturing plants. They are the preferred choice for mass - producing standard rear seats with high precision and efficiency. For example, in the production of popular car models, where thousands of rear seats need to be produced every day, automatic welding jigs can meet the high - volume demand.
Related Products
If you are interested in other automotive welding and checking fixtures, we also offer a wide range of products. You can check out our Automotive Seat Welding Fixture, which is designed to provide high - quality welding solutions for various types of automotive seats. Our Car Stamping Parts checking fixture is used to ensure the accuracy of car stamping parts, and the Front Bumper Welding Fixture is specifically designed for the welding of front bumpers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both manual and automatic rear seats welding jigs have their own advantages and disadvantages. Manual jigs are more flexible and cost - effective for small - scale production, while automatic jigs offer higher precision, efficiency, and safety for mass - production. When choosing between the two, you need to consider your production volume, quality requirements, budget, and the frequency of design changes.
If you are looking for a reliable rear seats welding jig supplier, we are here to help. We can provide you with professional advice and customized solutions based on your specific needs. Whether you need a manual or automatic welding jig, we have the expertise and experience to meet your requirements. Contact us today to start a discussion about your procurement needs, and let's work together to improve your automotive manufacturing process.
References
- Automotive Manufacturing Handbook, John Wiley & Sons
- Welding Technology and Applications, Prentice Hall
- Robotics in Automotive Production, Springer