An A Pillar welding fixture is a crucial tool in the automotive manufacturing industry, designed to hold and position A Pillar components accurately during the welding process. As a leading supplier of A Pillar welding fixtures, I understand the importance of these fixtures in ensuring high - quality welds and efficient production. In this blog, I will discuss the key components of an A Pillar welding fixture.
1. Base Structure
The base structure is the foundation of the A Pillar welding fixture. It provides stability and support for all other components. Usually made of high - strength steel or aluminum alloy, the base structure must be rigid enough to withstand the forces generated during the welding process.
The design of the base structure is also critical. It should be designed to allow easy access for the welding equipment and operators. For example, it may have open spaces or cut - outs to accommodate the movement of welding guns and robotic arms. Additionally, the base structure often includes mounting points for other components, such as clamping devices and locating pins.
2. Locating Pins and Bushings
Locating pins and bushings are essential for accurately positioning the A Pillar components. The pins are typically inserted into corresponding holes or slots in the components, while the bushings are installed in the fixture. This combination ensures that the components are placed in the correct position with high precision.
The size, shape, and location of the locating pins and bushings are carefully designed according to the specific requirements of the A Pillar components. They must be made of wear - resistant materials to ensure long - term accuracy. For instance, hardened steel is a common choice for these components.
3. Clamping Devices
Clamping devices are used to hold the A Pillar components firmly in place during the welding process. There are various types of clamping devices, including mechanical clamps, pneumatic clamps, and hydraulic clamps.
Mechanical clamps are simple and cost - effective. They use mechanical force, such as a screw or a lever, to apply pressure to the components. Pneumatic clamps, on the other hand, are powered by compressed air. They offer fast operation and can be easily integrated into automated production lines. Hydraulic clamps provide high clamping force and are suitable for heavy - duty applications.
The selection of clamping devices depends on factors such as the size and shape of the components, the required clamping force, and the production environment. For example, in a high - volume production line, pneumatic clamps may be preferred due to their speed and ease of automation.
4. Welding Guns and Torches
Welding guns and torches are the tools used to perform the actual welding. In an A Pillar welding fixture, the welding guns and torches need to be precisely positioned to ensure proper weld quality.
There are different types of welding processes used in A Pillar manufacturing, such as resistance spot welding and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding. Each process requires a specific type of welding gun or torch. For resistance spot welding, spot welding guns are used to create multiple weld spots on the A Pillar components. MIG welding torches, on the other hand, are used for continuous welds.
The welding guns and torches are often integrated with the fixture in a way that allows for easy movement and adjustment. They may be mounted on robotic arms or adjustable brackets to reach different welding positions on the A Pillar.
5. Robotic Systems
In modern automotive manufacturing, robotic systems play a significant role in A Pillar welding. Robotic arms can perform repetitive welding tasks with high precision and consistency.
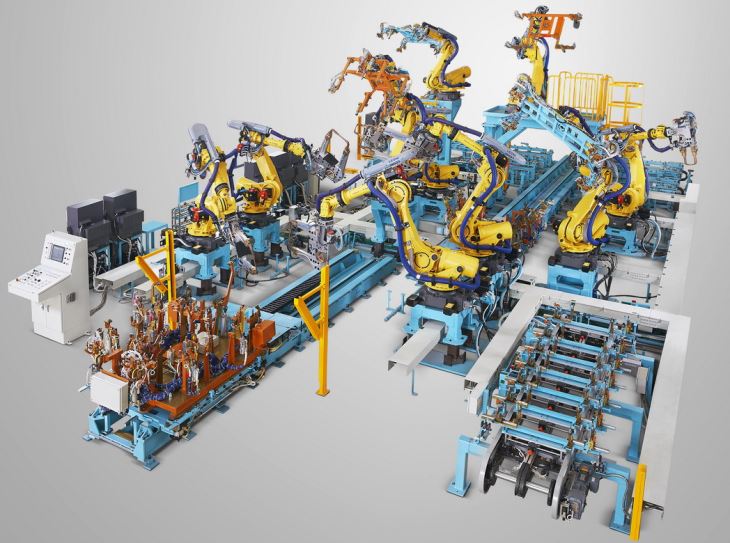

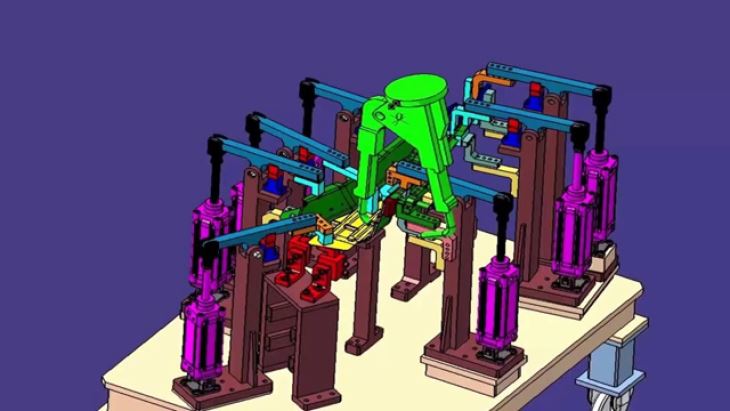
A robotic system used in an A Pillar welding fixture typically consists of a robotic arm, a controller, and a programming interface. The robotic arm is equipped with a welding gun or torch and can move in multiple axes to reach different parts of the A Pillar. The controller manages the movement and operation of the robotic arm, while the programming interface allows operators to define the welding paths and parameters.
Robotic systems offer several advantages, such as increased productivity, improved weld quality, and reduced labor costs. They can work continuously without fatigue and can be easily reprogrammed for different A Pillar designs. If you are interested in a more advanced solution, you can check out our Robotic Welding Fixture Line.
6. Sensor Systems
Sensor systems are used to monitor and control the welding process in an A Pillar welding fixture. They can detect various parameters, such as the position of the components, the welding current and voltage, and the temperature.
For example, position sensors can ensure that the A Pillar components are correctly located in the fixture. If a component is misaligned, the sensor can send a signal to the control system, which can then take corrective action. Welding current and voltage sensors can monitor the welding process to ensure that the welds are of high quality. Temperature sensors can detect overheating, which may indicate a problem with the welding process or the fixture.
The use of sensor systems helps to improve the reliability and quality of the A Pillar welding process. It allows for real - time monitoring and adjustment, reducing the risk of defective products.
7. Cooling Systems
Welding generates a significant amount of heat, which can affect the quality of the welds and the lifespan of the fixture components. Cooling systems are therefore essential in an A Pillar welding fixture.
There are different types of cooling systems, including air - cooling and water - cooling systems. Air - cooling systems use fans or blowers to circulate air around the welding area, dissipating heat. Water - cooling systems, on the other hand, use water to absorb and carry away the heat.
Water - cooling systems are generally more efficient than air - cooling systems, especially in high - heat applications. They can be designed to cool specific components, such as the welding guns and torches, or the entire fixture.
8. Tooling Plates and Changeover Mechanisms
In some cases, an A Pillar welding fixture may need to be used for different A Pillar designs. Tooling plates and changeover mechanisms are used to facilitate this flexibility.
Tooling plates are modular components that can be easily removed and replaced. They contain the locating pins, clamping devices, and other components specific to a particular A Pillar design. Changeover mechanisms allow for quick and easy switching between different tooling plates.
This modular design reduces the downtime required for reconfiguring the fixture for different products. It also increases the overall efficiency of the production line. If you are looking for a fixture that can handle different auto pillar parts, our Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture is a great option.
In conclusion, an A Pillar welding fixture is a complex and sophisticated tool that consists of multiple key components. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, efficiency, and quality of the A Pillar welding process. As a supplier, we are committed to providing high - quality A Pillar welding fixtures that meet the diverse needs of our customers. If you are in the automotive manufacturing industry and are looking for a reliable A Pillar welding fixture, please feel free to contact us for procurement and further discussions.
References
- Automotive Manufacturing Handbook, 3rd Edition
- Welding Technology and Applications, 2nd Edition
- Robotics in Manufacturing: Principles, Programming, and Applications




