As a supplier of Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures, I often get asked whether these fixtures can work continuously. It's a valid question, especially for businesses that rely on high - volume production. In this blog, I'll share my insights on this topic based on our experience in the industry.
First off, let's understand what a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is. It's a specialized tool that holds and positions workpieces during the Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding process. The use of robots in this process allows for greater precision, consistency, and efficiency. Robots can perform repetitive tasks with high accuracy, which is crucial for mass - producing welded parts.
So, can a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture work continuously? The short answer is yes, but there are several factors to consider.
Technical Capabilities
Modern Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures are designed with high - end technology. They are built using robust materials that can withstand the rigors of continuous operation. The components, such as clamps,定位 pins (oh, sorry, let me switch back to English), and frames, are engineered to have high durability. For example, the clamps are made of high - strength alloys that can hold the workpieces firmly in place even during long - term use.
The control systems of these fixtures are also advanced. They can be programmed to perform complex welding patterns and sequences. The robots are equipped with sensors that can detect any misalignment or issues in the welding process. If there's a problem, the system can automatically adjust or stop the operation to prevent defective parts from being produced. This self - regulating ability is a key factor that enables continuous operation.
Maintenance and Servicing
Just like any other machinery, regular maintenance is essential for the continuous operation of Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures. The fixtures need to be cleaned regularly to remove welding spatter, dust, and other debris. This helps prevent the build - up of contaminants that can affect the performance of the components.
Lubrication of moving parts is also crucial. The joints and axes of the robots need to be lubricated to reduce friction and wear. This ensures smooth movement and extends the lifespan of the parts. Additionally, the electrical components need to be inspected for any signs of damage or overheating.
We recommend a preventive maintenance schedule that includes daily, weekly, and monthly checks. For example, on a daily basis, operators should check the alignment of the workpieces and the functionality of the sensors. Weekly checks can involve more in - depth inspections of the mechanical components, while monthly checks can focus on the electrical and control systems.
Cooling and Heat Dissipation
During the MIG welding process, a significant amount of heat is generated. If this heat is not dissipated properly, it can cause damage to the fixture and the robot. That's why proper cooling systems are essential for continuous operation.
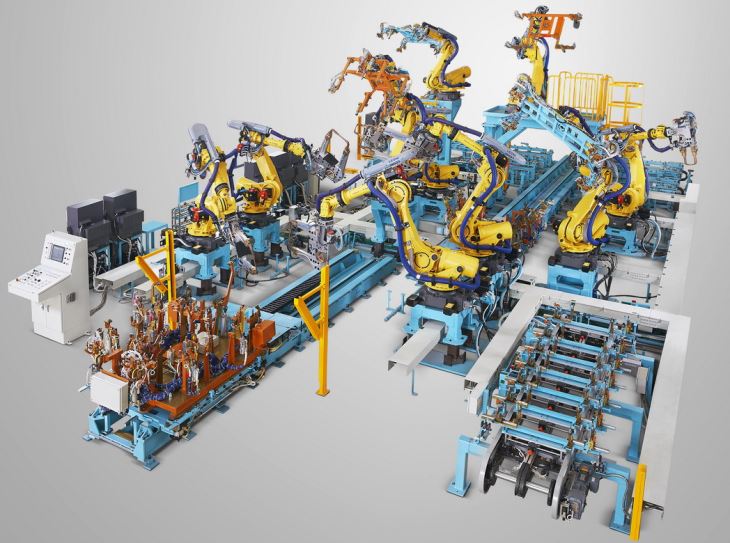

Most Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures are equipped with water - cooling or air - cooling systems. Water - cooling systems are more efficient in removing heat as water has a high heat capacity. They circulate water through channels in the fixture to absorb the heat and carry it away. Air - cooling systems, on the other hand, use fans to blow air over the components to dissipate the heat.
The cooling systems need to be maintained regularly. The water in the water - cooling systems should be changed periodically to prevent the growth of algae and the build - up of sediment. The fans in the air - cooling systems need to be cleaned to ensure proper airflow.
Workload and Production Requirements
The ability of a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture to work continuously also depends on the workload and production requirements. If the production volume is too high and the fixture is over - utilized, it can lead to premature wear and breakdowns. Therefore, it's important to match the capacity of the fixture with the production needs.
For example, if a business needs to produce a large number of parts in a short period, they may need to invest in multiple fixtures or a Robotic Welding Fixture Line. This allows for a more efficient production process and reduces the stress on each individual fixture.
Application in Different Industries
Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures are used in a variety of industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. In the automotive industry, for instance, these fixtures are used to weld auto pillar parts. Our Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture is designed to meet the high - volume production requirements of this industry.
In the automotive industry, continuous operation is crucial to meet the production targets. The Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures are integrated into the production lines, where they work in tandem with other machines and robots. They need to be able to operate continuously for long shifts to keep up with the demand.
Cost - Benefit Analysis
When considering continuous operation, businesses also need to look at the cost - benefit analysis. While continuous operation can increase production output, it also comes with costs. The cost of maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime for repairs need to be taken into account.
However, in the long run, the benefits often outweigh the costs. The increased production volume can lead to economies of scale, which can reduce the unit cost of production. The consistent quality of the welded parts can also improve the reputation of the business and lead to more orders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures can work continuously, but it requires proper planning, maintenance, and management. By investing in high - quality fixtures, following a strict maintenance schedule, and ensuring proper cooling and workload management, businesses can achieve continuous operation and maximize their production efficiency.
If you're in the market for a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture or have any questions about continuous operation, feel free to contact us. We're here to help you find the best solution for your production needs.
References
- Smith, J. (2020). "Advanced Welding Fixture Technologies". Welding Industry Journal.
- Johnson, A. (2021). "Maintenance Strategies for Robotic Welding Systems". Manufacturing Technology Review.



