As a supplier of A PILLAR welding fixtures, I'm often asked about the technical specifications of these essential tools in the automotive manufacturing process. In this blog post, I'll delve into the key aspects that define the performance, quality, and suitability of A PILLAR welding fixtures.
1. Structural Design
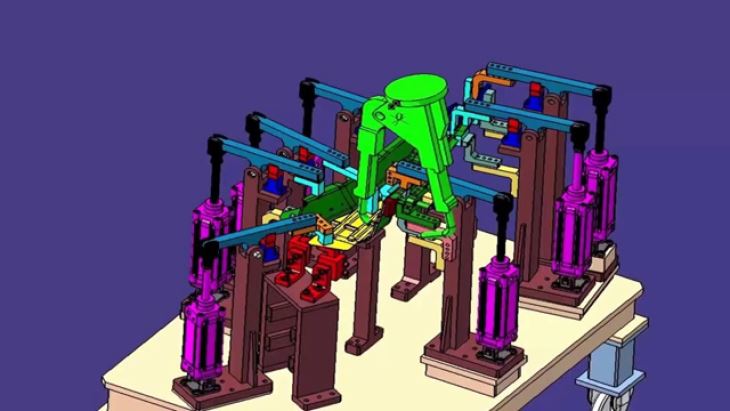
The structural design of an A PILLAR welding fixture is crucial for its functionality. It must be able to securely hold the A PILLAR components in place during the welding process, ensuring precise alignment and preventing any movement that could lead to welding defects.
- Material Selection: High - strength steel is commonly used for the main frame of the fixture. This material provides the necessary rigidity to withstand the forces exerted during welding. For example, 4140 alloy steel is a popular choice due to its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and good toughness.
- Modular Design: Many modern A PILLAR welding fixtures feature a modular design. This allows for easy customization and adaptation to different A PILLAR models. Modules can be easily replaced or reconfigured, reducing downtime and increasing the fixture's versatility. For instance, a fixture can have interchangeable clamping modules that can be adjusted according to the thickness and shape of the A PILLAR components.
2. Clamping System
The clamping system is one of the most critical parts of an A PILLAR welding fixture. It is responsible for firmly holding the A PILLAR components in the correct position.
- Hydraulic Clamps: Hydraulic clamps are widely used in A PILLAR welding fixtures due to their high clamping force and precise control. They can quickly and securely hold the components, even under high - pressure welding conditions. For example, a hydraulic clamp with a clamping force of up to 5000 N can ensure that the A PILLAR components remain stable during the welding process.
- Pneumatic Clamps: Pneumatic clamps are also popular, especially in applications where a relatively lower clamping force is required. They are lightweight, easy to operate, and cost - effective. Pneumatic clamps can be controlled by a simple air compressor system, making them suitable for small - to - medium - scale manufacturing operations.
- Adjustable Clamps: To accommodate different A PILLAR sizes and shapes, adjustable clamps are often incorporated into the fixture design. These clamps can be adjusted in multiple directions, allowing for precise positioning of the components. For example, an adjustable clamp can be moved horizontally, vertically, and angularly to ensure a perfect fit for the A PILLAR.
3. Positioning Accuracy
Positioning accuracy is a key factor in the quality of the welded A PILLAR. The fixture must be able to position the components with high precision to ensure proper alignment and weld quality.
- Guide Pins and Bushings: Guide pins and bushings are commonly used to ensure accurate positioning of the A PILLAR components. These pins and bushings are precisely machined to have a tight fit, guiding the components into the correct position. For example, a guide pin with a tolerance of ±0.05 mm can ensure that the A PILLAR components are positioned accurately within the fixture.
- Laser Alignment Systems: Some advanced A PILLAR welding fixtures are equipped with laser alignment systems. These systems use lasers to measure and adjust the position of the components in real - time, ensuring high - precision positioning. Laser alignment systems can detect even the slightest misalignment and make adjustments automatically, improving the overall quality of the welded A PILLAR.
4. Weld Accessibility
The design of the A PILLAR welding fixture must also consider weld accessibility. The fixture should allow easy access for the welding equipment to reach all the necessary welding points.
- Open - Frame Design: An open - frame design is often preferred for A PILLAR welding fixtures. This design provides clear access to the welding areas, allowing the welding torch to move freely around the A PILLAR components. For example, an open - frame fixture can have large openings and clearances, ensuring that the welding torch can reach all the corners and joints of the A PILLAR.
- Rotating and Tilting Mechanisms: Some fixtures are equipped with rotating and tilting mechanisms to improve weld accessibility. These mechanisms allow the A PILLAR components to be rotated or tilted to the optimal position for welding. For instance, a rotating mechanism can rotate the A PILLAR by 360 degrees, enabling the welding torch to access all sides of the component without any obstructions.
5. Compatibility with Welding Processes
The A PILLAR welding fixture must be compatible with the specific welding processes used in the manufacturing.
- Resistance Spot Welding: For resistance spot welding, the fixture must be designed to provide good electrical conductivity and proper electrode placement. The fixture should have conductive materials and well - designed electrode holders to ensure efficient and high - quality spot welding. For example, the fixture can be made of copper - alloy materials to improve electrical conductivity.
- MIG/MAG Welding: In MIG/MAG welding applications, the fixture should allow for easy wire feeding and shielding gas flow. It should also be designed to minimize the interference with the welding torch movement. For instance, the fixture can have channels for wire feeding and gas distribution, ensuring a smooth welding process.
6. Durability and Maintenance
Durability and ease of maintenance are important considerations for A PILLAR welding fixtures.
- Surface Treatment: To enhance durability, the fixture components are often subjected to surface treatments such as plating or coating. For example, a zinc - plating treatment can protect the steel components from corrosion, increasing their service life.
- Modular Replaceable Parts: As mentioned earlier, modular design also facilitates maintenance. Modular replaceable parts can be easily removed and replaced when they are worn out or damaged, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For example, a worn - out clamping module can be quickly replaced with a new one, without the need to replace the entire fixture.
7. Automation and Integration
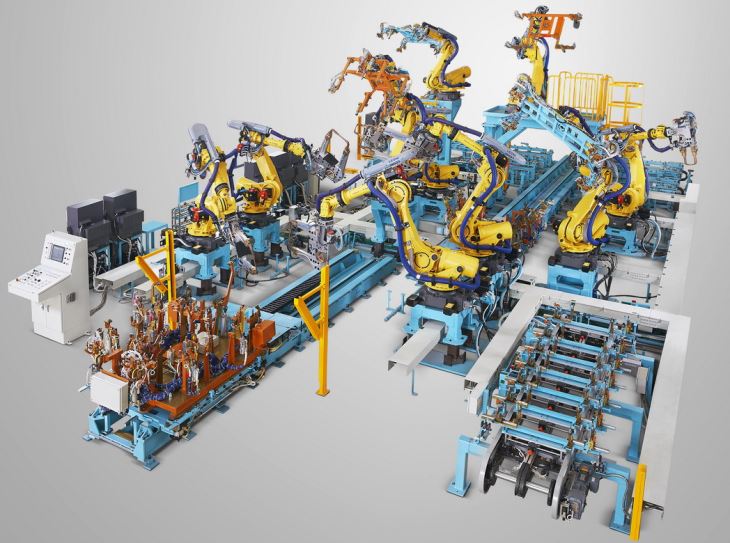
In modern automotive manufacturing, automation and integration are becoming increasingly important. A PILLAR welding fixtures can be integrated into automated production lines for increased efficiency and productivity.
- Robotic Welding: A PILLAR welding fixtures can be designed to work in conjunction with robotic welding systems. The fixture should be compatible with the robot's movement and programming, allowing for seamless integration. For example, the fixture can have sensors and interfaces that communicate with the robot, enabling precise control of the welding process.
- Conveyor Systems: Fixtures can also be integrated with conveyor systems to facilitate the continuous flow of A PILLAR components through the welding process. This integration can improve the overall production efficiency and reduce manual handling. For instance, a conveyor system can transport the A PILLAR components to the welding station and then move them to the next processing step after welding.
If you are in the market for high - quality A PILLAR welding fixtures, we are here to offer you the best solutions. Our fixtures are designed and manufactured to meet the highest technical standards, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. We can also provide customized solutions to meet your specific requirements. For more information about our Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture and Robotic Welding Fixture Line, please feel free to contact us for procurement and negotiation.

References
- "Automotive Welding Fixture Design and Manufacturing" - Industry Handbook
- "Advanced Welding Technologies in Automotive Manufacturing" - Research Paper
- "Principles of Fixture Design for Precision Manufacturing" - Academic Journal Article




