Hey there! As a supplier of Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures, I've got a ton of hands - on experience when it comes to understanding the ins and outs of the welding process. One crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the welding gas used in these fixtures. In this blog, I'll break down the requirements for the welding gas in a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture.
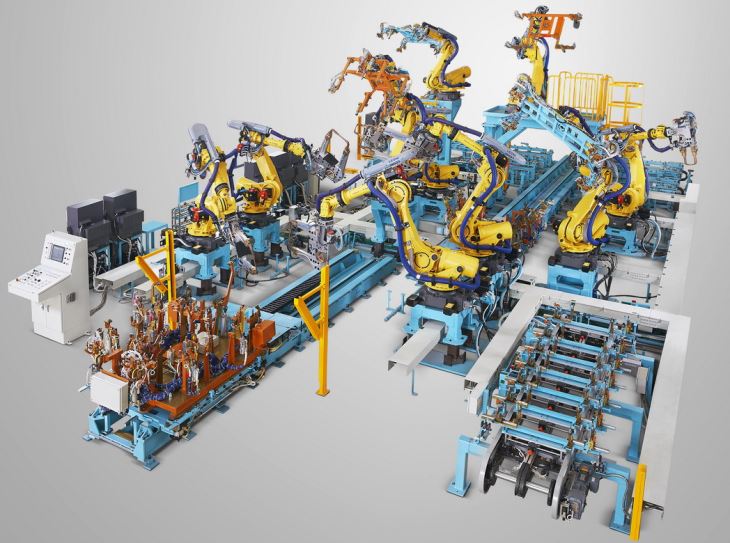

1. Shielding Purpose
The primary job of welding gas in a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture is to shield the weld pool. When we're welding, the high - temperature arc causes the metal to melt, and at this time, the molten metal is extremely reactive. If it comes into contact with the oxygen and nitrogen in the air, it can lead to some major problems. Oxygen can cause oxidation, which results in a brittle and porous weld. Nitrogen can also cause porosity and reduce the ductility of the weld.
So, we need a gas that can create a protective barrier around the weld pool. This shielding gas displaces the air and prevents these harmful reactions from taking place. For example, argon is a popular choice for shielding gas because it's an inert gas. It doesn't react with the molten metal, so it provides a clean and stable environment for welding. You can check out our Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture to see how this shielding gas works in a real - world application.
2. Arc Stability
Another key requirement for the welding gas is to ensure arc stability. A stable arc is essential for a high - quality weld. If the arc is unstable, it can lead to inconsistent weld bead shape, spatter, and poor penetration.
Different gases have different effects on arc stability. Argon, as mentioned earlier, provides a smooth and stable arc. However, pure argon might not be suitable for all types of metals. For welding steel, adding a small amount of carbon dioxide (CO₂) to argon can improve the arc characteristics. CO₂ helps to increase the heat input and penetration of the weld. But too much CO₂ can cause more spatter. So, finding the right balance is crucial.
Our Robotic Welding Fixture Line is designed to work with a variety of welding gases to achieve optimal arc stability. We've done extensive testing to make sure that the fixtures can handle different gas mixtures and still produce top - notch welds.
3. Weld Quality
The quality of the weld is directly affected by the welding gas. A good welding gas should help to produce a weld with proper penetration, good fusion, and minimal defects.
Penetration is important because it determines how well the weld joins the base metals. The right gas mixture can control the heat distribution and ensure that the weld penetrates deep enough without over - heating the surrounding area. Fusion is about how well the molten metal mixes with the base metal. A stable shielding gas helps to create a smooth and uniform fusion zone.
Defects like porosity, cracks, and inclusions can seriously weaken the weld. By using the correct welding gas, we can minimize these defects. For example, helium can be added to the gas mixture in some cases. Helium has a high heat - carrying capacity, which can increase the welding speed and improve the bead appearance. But it's also more expensive than argon, so we need to consider the cost - benefit ratio.
4. Compatibility with Metals
Not all welding gases are suitable for all metals. Different metals have different chemical and physical properties, and they require specific gas mixtures for optimal welding.
For aluminum welding, pure argon is often the best choice. Aluminum is highly reactive, and argon provides a clean and non - reactive environment. It helps to prevent oxidation and produces a smooth and shiny weld.
When it comes to stainless steel, a mixture of argon and a small amount of CO₂ or oxygen can be used. This mixture helps to improve the arc stability and the wetting action of the weld, resulting in a better - looking and stronger weld.
For mild steel, argon - CO₂ mixtures are commonly used. The CO₂ increases the heat input and penetration, while the argon provides shielding and arc stability.
5. Flow Rate
The flow rate of the welding gas is also an important factor. If the flow rate is too low, the shielding gas won't be able to effectively displace the air around the weld pool, leading to oxidation and porosity. On the other hand, if the flow rate is too high, it can cause turbulence, which can also introduce air into the weld pool and create defects.
The ideal flow rate depends on several factors, such as the type of welding process, the size of the welding nozzle, and the welding speed. Generally, for MIG welding, a flow rate between 15 - 30 cubic feet per hour (CFH) is common. But we need to adjust it according to the specific situation.
6. Cost - Effectiveness
Let's face it, cost matters. As a supplier, we always want to provide our customers with the best - quality products at a reasonable price. When choosing the welding gas, we need to consider the cost - effectiveness.
Some gases, like helium, are more expensive than others. While helium has some advantages, such as high heat - carrying capacity, we need to weigh the benefits against the cost. In many cases, a well - balanced argon - CO₂ mixture can provide a good combination of performance and cost.
We understand that our customers are looking for the best value for their money. That's why we've designed our Robotic MIG Weld Fixtures to work efficiently with different gas mixtures, allowing our customers to choose the most cost - effective option for their specific welding needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the requirements for the welding gas in a Robotic MIG Weld Fixture are multi - faceted. We need a gas that can shield the weld pool, ensure arc stability, improve weld quality, be compatible with different metals, have an appropriate flow rate, and be cost - effective.
If you're in the market for a high - quality Robotic MIG Weld Fixture and want to learn more about how the right welding gas can enhance your welding process, don't hesitate to reach out. We're here to help you make the best choices for your welding projects. Whether you're working on Auto Pillar Parts Welding Fixture or Robotic Welding Fixture Line, we've got the expertise and the products to meet your needs. Contact us today to start a discussion about your specific requirements and how we can help you achieve top - notch welding results.
References
- O'Keefe, M. (2019). Welding Gases: Selection and Application. Industrial Press.
- American Welding Society. (2017). AWS Welding Handbook, Volume 2: Welding Processes.



